WebKit for Developers
 For many of us developers, WebKit is a black box. We throw HTML, CSS, JS and a bunch of assets at it, and WebKit, somehow.. magically, gives us a webpage that looks and works well. But in fact, as my colleague Ilya Grigorik puts it…
For many of us developers, WebKit is a black box. We throw HTML, CSS, JS and a bunch of assets at it, and WebKit, somehow.. magically, gives us a webpage that looks and works well. But in fact, as my colleague Ilya Grigorik puts it…
WebKit isn’t a black box. It’s a white box. And not just that, but an open, white box.
So let’s take a moment to understand some things:
What isn’t WebKit?
How is WebKit used by WebKit-based browsers?
Why are all WebKits not the same?
Now, especially with the news that Opera has moved to WebKit, we have a lot of WebKit browsers out there, but its pretty hard to know what they share and where they part ways. Below we’ll hopefully shine some light on this. As a result you’ll be able to diagnose browser differences better, report bugs at the right tracker, and understand how to develop against specific browsers more effectively.
Standard Web Browser Components
Let’s lay out a few components of the modern day web browser:
- Parsing (HTML, XML, CSS, JavaScript)
- Layout
- Text and graphics rendering
- Image decoding
- GPU interaction
- Network access
- Hardware acceleration
Which of those are shared in WebKit-based browsers? Pretty much only the first two.
The others are handled by individual WebKit ports. Let’s review what that means…
The WebKit Ports
There are different “ports” of WebKit, but allow me to let Ariya Hidayat, WebKit hacker and eng director at Sencha to explain:
What is the popular reference to WebKit is usually Apple’s own flavor of WebKit which runs on Mac OS X (the first and the original WebKit library). As you can guess, the various interfaces are implemented using different native libraries on Mac OS X, mostly centered around CoreFoundation. For example, if you specify a flat colored button with specific border radius, well WebKit knows where and how to draw that button. However, the final actual responsibility of drawing the button (as pixels on the user’s monitor) falls into CoreGraphics.
As mentioned above, using CG is unique to the Mac port. Chrome on Mac uses Skia here.
With time, WebKit was “ported” into different platform, both desktop and mobile. Such flavor is often called “a WebKit port”. For Safari Windows, Apple themselves also ported WebKit to run on Windows, using the Windows version of its (limited implementation of) CoreFoundation library.
… though Safari for Windows is now dead.
Beside that, there were many other “ports” as well (see the full list). Google has created and continues to maintain its Chromium port. There is also WebKitGtk which is based on Gtk+. Nokia (through Trolltech, which it acquired) maintains the Qt port of WebKit, popular as its QtWebKit module.
Some of the ports of WebKit
- Safari
- Safari for OS X and Safari for Windows are two different ports
- WebKit nightly is an edge build of the Mac port that’s used for Safari. More later…
- Mobile Safari
- Maintained in a private branch, but lately being upstreamed
- Chrome on iOS (using Apple’s WebView; more on it’s differences later)
- Chrome (Chromium)
- Chrome on Android (using the Chromium port directly)
- Chromium also powers Yandex Browser, 360 Browser, Sogou Browser, and soon, Opera.
- Android Browser
- Used the latest WebKit source at the time
- Plenty more ports: Amazon Silk, Dolphin, Blackberry, QtWebKit, WebKitGTK+, The EFL port (Tizen), wxWebKit, WebKitWinCE, etc
Different ports can have different focuses. The Mac port’s focus is split between Browser and OS, and introduces Obj-C and C++ bindings to embed the renderer into native applications. Chromium’s focus is purely on the browser. QtWebKit offers its port for applications to use as a runtime or rendering engine within its cross-platform GUI application architecture.
What’s shared in all WebKit browsers
First, let’s review the commonalities shared by all WebKit ports.
- So first, WebKit parses HTML the same way. Well, except Chromium is the only port so far to enable threaded HTML parsing support.
- … Okay, but once parsed, the DOM tree is constructed the same. Well, actually Shadow DOM is only turned on for the Chromium port, so DOM construction varies. Same goes for custom elements.
- … Okay, well WebKit creates a
windowobject anddocumentobject for everyone. True, though the properties and constructors it exposes can be conditional on the feature flags enabled. - … CSS parsing is the same, though. Slurping up your CSS and turning it into CSSOM’s pretty standard. Yeah, though Chrome accepts just the
-webkit-prefix whereas Apple and other ports accept legacy prefixes like-khtml-and-apple-. - … Layout.. positioning? Those are the bread and butter. Same, right? Come on! Sub-pixel layout and saturated layout arithmetic is part of WebKit but differs from port to port.
- Super.
Just like how Flickr and Github implement features behind flags, WebKit does the same. This allows ports to enable/disable all sorts of functionality with WebKit’s compile-time Feature Flags. Features can also be exposed as run-time flags either through command line switches (Chromium’s here) or configuration like about:flags.
All right, well let’s try again to codify what’s the same in WebKit land…
What’s common to every WebKit port
- The DOM,
window,document- more or less
- The CSSOM
- CSS parsing, property/value handling
- sans vendor prefix handling
- HTML parsing and DOM construction
- same if we suspended belief in Web Components
- All layout and positioning
- Flexbox, Floats, block formatting contexts… all shared
- The UI and instrumentation for the Chrome DevTools aka WebKit Inspector.
- Though since last April, Safari uses it’s own, non-WebKit, closed-source UI for Safari Inspector
- Features like contenteditable, pushState, File API, most SVG, CSS Transform math, Web Audio API, localStorage
- Though backends vary. Each port may use a different storage layer for localStorage and may use different audio APIs for Web Audio API.
- Plenty of other features & functionality
It gets a little murky in those areas. Let’s try some differences that are much less murky.
Now, what’s not shared in WebKit ports:
- Anything on the GPU
- 3D Transforms
- WebGL
- Video decoding
- 2D drawing to the screen
- Antialiasing approaches
- SVG & CSS gradient rendering
- Text rendering & hyphenation
- Navigating back/forward
- The navigation parts of pushState()
<video>&<audio>element behavior (and codec support)- Network stack (SPDY, prerendering, WebSocket transport)
- SSL features like Strict Transport Security and Public Key Pins
- A JavaScript engine
- JavaScriptCore is in the WebKit repo. There are bindings in WebKit for both it and V8
- Rendering of form controls
- Image decoding
Let’s take one of these: 2D graphics Depending on the port, we’re using completely different libraries to handle drawing to screen:
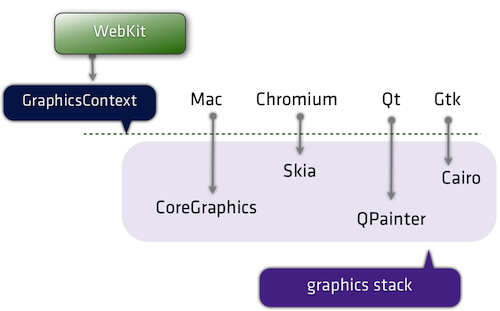
Or to go a little more micro… a recently landed feature: CSS.supports() was enabled for all ports except win and wincairo, which don’t have css3 conditional features enabled.
Now that we’ve gotten technical.. time to get pedantic. Even the above isn’t correct. It’s actually WebCore that’s shared. “WebKit” is technically the binding layer between WebCore and the ports.
A diagram should help:
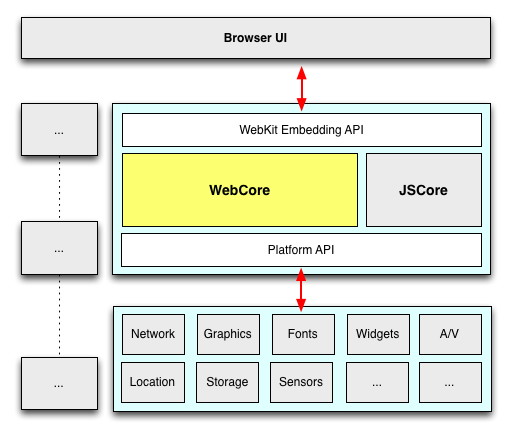
Many of the components within WebKit are swappable (shown above in gray).
As an example, WebKit’s JavaScript engine, JavaScriptCore, is a default in WebKit. (It is based originally on KJS (from KDE) back when WebKit started as a fork of KHTML). Meanwhile, the Chromium port swaps in V8 here, and uses unique DOM bindings to map things over.
Fonts and Text rendering is a huge part of platform. There are 2 separate text paths in WebKit: Fast and Complex. Both require platform-specific (port-side) support, but Fast just needs to know how to blit glyphs (which WebKit caches for the platform) and complex actually hands the whole string off to the platform layer and says “draw this, plz”.
“WebKit is like a Sandwich. Though in Chromium’s case it’s more like a taco. A delicious web platform taco.” Dimitri Glazkov, Chrome WebKit hacker. Champion of Web Components and Shadow DOM
Now, let’s widen the lens and look at a few ports and a few subsystems. Below are five ports of WebKit; consider how varied their stacks are, despite sharing much of WebCore.
| Chrome (OS X) | Safari (OS X) | QtWebKit | Android Browser | Chrome for iOS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rendering | Skia | CoreGraphics | QtGui | Android stack/Skia | CoreGraphics |
| Networking | Chromium network stack | CFNetwork | QtNetwork | Fork of Chromium’s network stack | Chromium stack |
| Fonts | Skia | CoreText | Qt internals | Android stack | CoreText |
| JavaScript | V8 | JavaScriptCore | JSC (V8 is used elsewhere in Qt) | V8 | JavaScriptCore (without JITting) * |
* A side note on Chrome for IOS. It uses UIWebView, as you likely know. Due to the capabilities of UIWebView that means it can only use the same rendering layer as Mobile Safari, JavaScriptCore (instead of V8) and a single-process model. Still, considerable Chromium-side code is leveraged, such as the network layer, the sync and bookmarks infrastructure, omnibox, metrics and crash reporting. (Also, for what it’s worth, JavaScript is so rarely the bottleneck on mobile that the lack of JITting compiler has minimal impact.)
All right, so where does this leave us?
So, all WebKits are totally different now. I’m scared.
Don’t be! The layoutTest coverage in WebKit is enormous (28,000 layoutTests at last count), not only for existing features but for any found regressions. In fact, whenever you’re exploring some new or esoteric DOM/CSS/HTML5-y feature, the layoutTests often have fantastic minimal demos of the entire web platform.
In addition, the W3C is ramping up its effort for conformance suite testing. This means we can expect both different WebKit ports and all browsers to be testing against the same suite of tests, leading to fewer quirks and a more interoperable web. For all those who have assisted this effort by going to a Test The Web Forward event… thank you!
Opera just moved to WebKit. How does that play out?
Robert Nyman and Rob Hawkes touched on this, too, but I’ll add that one of the signifcant parts of Opera’s announcement was that Opera adopted Chromium. This means the WebGL, Canvas, HTML5 forms, 2D graphics implementations–all that stuff will be the same on Chrome and Opera now. Same APIs, and same backend implementation. Since Opera is Chromium-based, you can feel confident that your cutting-edge work will be compatible with Chrome and Opera simultaneously.
I should also point out that all Opera browsers will be adopting Chromium. So Opera for Windows, Mac and Linux and Opera Mobile (the fully fledged mobile browser). Even Opera Mini, the thin client, will be swapping out the current server-side rendering farm based on Presto with one based on Chromium.
.. and the WebKit Nightly. What is that?
It’s the mac port of WebKit, running inside of the same binary that Safari uses (though with a few underlying libraries swapped out). So its behavior and feature set is congruent with what you’ll find in Safari. If you want to go back to middle-school analogies, think of it as… WebKit Nightly is to Safari what Chromium is to Chrome.
Chrome Canary also has the latest WebKit source within a day or so.
Tell me more about WebKit internals.
You got it, bucko.
Further reading:
- WebKit internals technical articles | webkit.org
- WebKit: An Objective View | Robert Nyman & Rob Hawkes
- your webkit port is special (just like every other port) | Ariya Hidayat
- Getting Started With the WebKit Layout Code | Adobe Web Platform Blog
- WebKit Documentation Overview | Arun Patole
- Rendering in WebKit, by Eric Seidel | YouTube
- web performance for the curious | Ilya Grigorik
Hopefully this article described a bit of the internals of WebKit browsers and gave some insight on where the WebKit ends and the ports begin.
Reviewed by Peter Beverloo (Chrome), Divya Manian (Adobe), Eric Seidel (WebKit).
I’ll update with any corrections or modifications.